451 Research: Data in Motion – What’s Driving Industries Toward Unified Data?

In the last few years, messaging and event stream processing technologies have gone from niche products reserved mainly for industries such as financial services and telecommunications to core components of modern data architecture. Several factors have driven this change, including the explosion of open-source projects that have reduced costs and barriers to entry, the growth of microservices-based architecture and broader recognition of the strategic value of real-time data processing and analysis.
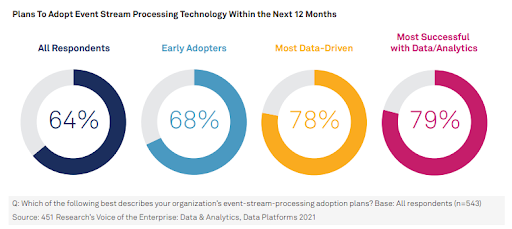
According to survey data from 451 Research, nearly 64% of companies have either adopted event stream processing technology or plan to adopt it within the next 12 months. This percentage is even higher among companies that are most data-driven and those that have been most successful with their data and analytics. Let's take a closer look at how modern event streaming technology is transforming the enterprise.
Blending Data Volume With Data Scaling
Enterprises deal not only with significant data volumes coming in, such as with event steaming systems, but also with the ability to land all of this incoming data. Event streaming systems, which often produce large data volumes compared with systems adding data in part and parcel, require an underlying architecture that can scale dynamically to avoid potential data loss and can also store the data such that it can be accessed in a multitude of ways.
Enabling Real-Time and Ad Hoc Data Processing, and Accessing Data in Cohesion
Accommodating large data volumes and scaling is one thing; accessing that data—in the ways enterprises need to—is quite another. Because event streaming systems continuously process data, enterprises need to access the data in real time, no matter how much data comes in. This is critical for time-sensitive applications like fraud detection, SIEM and proactive monitoring, where even a five-minute delay is five minutes too long. Likewise, processing data soon after landing can be useful as well, especially for driving reports, dashboards and ad hoc analytics. But enterprises also value data processing, particularly time-series data, for carrying out analysis on data during a set time frame or multiple time frames.
Microservices
A challenge that can arise with microservices-based architectures is coupling, or interdependence, between software systems, whereby a change in one system necessitates a change in another. With more microservices, this coupling can be compounded, resulting in complex and costly architectures. Event stream processing addresses this issue through the decoupling of these systems, having some systems publish events and others subscribe to them. This gives enterprises the flexibility to scale their architecture with minimal system changes.
Unified Data Architecture for Event Streaming
Thanks to the free availability of open-source projects and the growing prevalence of technologies such as microservices-based architecture, messaging and event stream processing has become an integral part of modern data architecture. Enterprises that once had to gather a variety of technologies to design their architecture now have access to open-source projects like Apache Pulsar that enable them to replace multiple specialized technologies with a single messaging and event streaming platform.
- Copyright © 2021 S&P Global Market Intelligence.
- The content of this artifact is for educational purposes only. 451 Research, S&P Global Market Intelligence does not endorse any companies, technologies, products, services, or solutions. Permission to reprint or distribute any content from this artifact requires the prior written approval of S&P Global Market Intelligence.





