What is Hybrid Cloud?
Hybrid cloud is defined as a computing environment that incorporates infrastructure from multiple platforms and data centers. Most often, it’s a combination of on-premises resources with those offered by a cloud service provider. But it could also consist of multiple cloud platforms and services with no on-premises component.
What is Hybrid Cloud? | Hybrid Cloud Database
Introduction to hybrid cloud architecture
Cloud computing is everywhere and will continue to grow. However, tooling incompatibilities, security constraints, or cost considerations could prevent some components from moving to the cloud.
Since the start of modern cloud computing in 2006, the cloud industry has erupted into a $153 ≈billion market, projected by Gartner to grow more than 21 percent per year. This next generation model for server and compute resource consumption embodied a fundamental shift for enterprise companies, and a new surface for them to build applications and services. Before the cloud came into play, the on-premises data center, hosted within a company's walls, was the only option. At that time, IT departments were responsible for acquiring and configuring the machinery to power the organization's technological front.
When the cloud was first introduced, its reliability and security was met with significant skepticism. But, as time marched on, cloud service providers such as Amazon, Microsoft, Google, and IBM poured engineering grit into their cloud products. And popular applications, such as Netflix, declared they were running workloads off-premises. These early adopters had the luxury of growing up in a cloud world– For them, the time-to-market benefit from deploying in the cloud far outweighed the time and cost it would take to build an on-premises data center.
But what about the case where a successful foundation was already in place, with an in-house technology infrastructure, and millions were already invested? Should companies in that position fight to maintain the status quo?
- Consider the cost savings Dropbox enjoyed after building its own technology infrastructure and moving away from the public cloud.
- What about the proliferation of developer tooling found among the public and private clouds? It often causes internal strife over which cloud to choose for a given task.
- And don't forget about the security and governance concerns when placing sensitive information in data centers that are not hosted in-house.
The paradox of choice defines the cloud world, with a sea of options that are difficult to navigate and decipher. Today's business needs continue to demand a cloud strategy. These challenges are here to stay, making a hybrid cloud strategy the core focus for innovators and decision-makers within every enterprise.
How do leading companies define hybrid cloud?
The technology sector moves faster than most, and the cloud age is at a stage of rapid transformation. Thought leaders are striving to define the terminology and jargon used to describe this evolving ecosystem. Communication in this environment can be difficult, as common terms have not reached an established standard.
To help you understand exactly how hybrid cloud is being defined, we've collected definitions from top companies across the technology landscape. Let's take a look!
IBM
According to IBM, a hybrid cloud uses a private cloud foundation combined with the strategic integration and use of public cloud services.
RedHat
RedHat defines a hybrid cloud as a combination of one or more public and private clouds orchestrated by management and automation software that allows workloads, resources, platforms, and applications to migrate between environments.
Gartner
According to Gartner, hybrid cloud refers to policy-based and coordinated service provisioning, use, and management across a mixture of internal and external cloud services.
ZDNet
ZDNet defines a hybrid cloud as one or more public clouds connected to something in my data center. That thing could be a private cloud, that thing could just be traditional data center infrastructure.
Amazon
At Amazon, hybrid cloud refers to the use of both on-premises resources in addition to public cloud resources.
Microsoft
Microsoft defines a hybrid cloud as a computing environment that combines a public cloud and a private cloud by allowing data and applications to be shared between them.
Understanding the different types of cloud database technologies
As the name suggests, hybrid cloud is a mixture of multiple cloud types and deployments.
Let's review the options: on-premises, public cloud, private cloud, hybrid cloud, and multi-cloud.
On-premises
Technology resources, data centers, and sources that are hosted within a company's infrastructure. Typically, this means that the company purchased hardware and is connected via a private network.
Learn more about on-premises challenges
Public cloud
Technology resources, data centers, and sources that are hosted by a cloud service provider off-premises. These reside alongside other resources that are not occupied by a single company and are accessible via the public internet.
Take a look at our resources about three leading public cloud providers: Microsoft Azure, Amazon Web Services, and Google Cloud.
Private cloud
Technology resources, data centers and sources that are hosted either by a cloud service provider off-premises or within a company's infrastructure. Typically, this is in conjunction with deployment management, container, and virtual machine technologies. Solutions like VMware, OpenStack, and Kubernetes are often in the mix. These resources are only available and accessible to a single company via a private network.
Learn more about the private cloud with our series of videos from Accelerate
Hybrid cloud
Technology resources, data centers and sources that incorporate infrastructure from multiple environments. Most often, it's a combination of on-premises resources and those offered by cloud service providers. It also likely includes multiple cloud platforms.
This deployment opens up a range of new use cases
Multi-cloud
Technology resources, data centers, and sources distributed across multiple cloud service providers and on-premises resources. Unlike intercloud setups, multi-cloud does not involve traffic between the cloud service providers. Instead, connectivity between the cloud-service providers and on-premises resources may be established through a private network. Multi-cloud is considered a subset of hybrid cloud.
Understand why multi-cloud is good for your data
Comparing cloud architectures
| On-Premises | Single Cloud | Hybrid Cloud | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ability to keep sensitive data in-house | ✔ | X | ✔ |
| Flexible access to global footprint | X | ✔ | ✔ |
| Choice of best of breed technology options | X | X | ✔ |
| High availability / disaster recovery | X | X | ✔ |
| Optimal control over SLAs | ✔ | X | ✔ |
| No complexity of managing across clouds | ✔ | ✔ | X |
| Avoid vendor lock-in / data autonomy / keep negotiating leverage | ✔ | X | ✔ |
| Easy to accommodate infrastructure of acquired businesses | X | X | ✔ |
A closer look at hybrid cloud
Gartner defines four different cloud deployment models that IT organizations are implementing, and all of them have some form of hybrid cloud at their core.
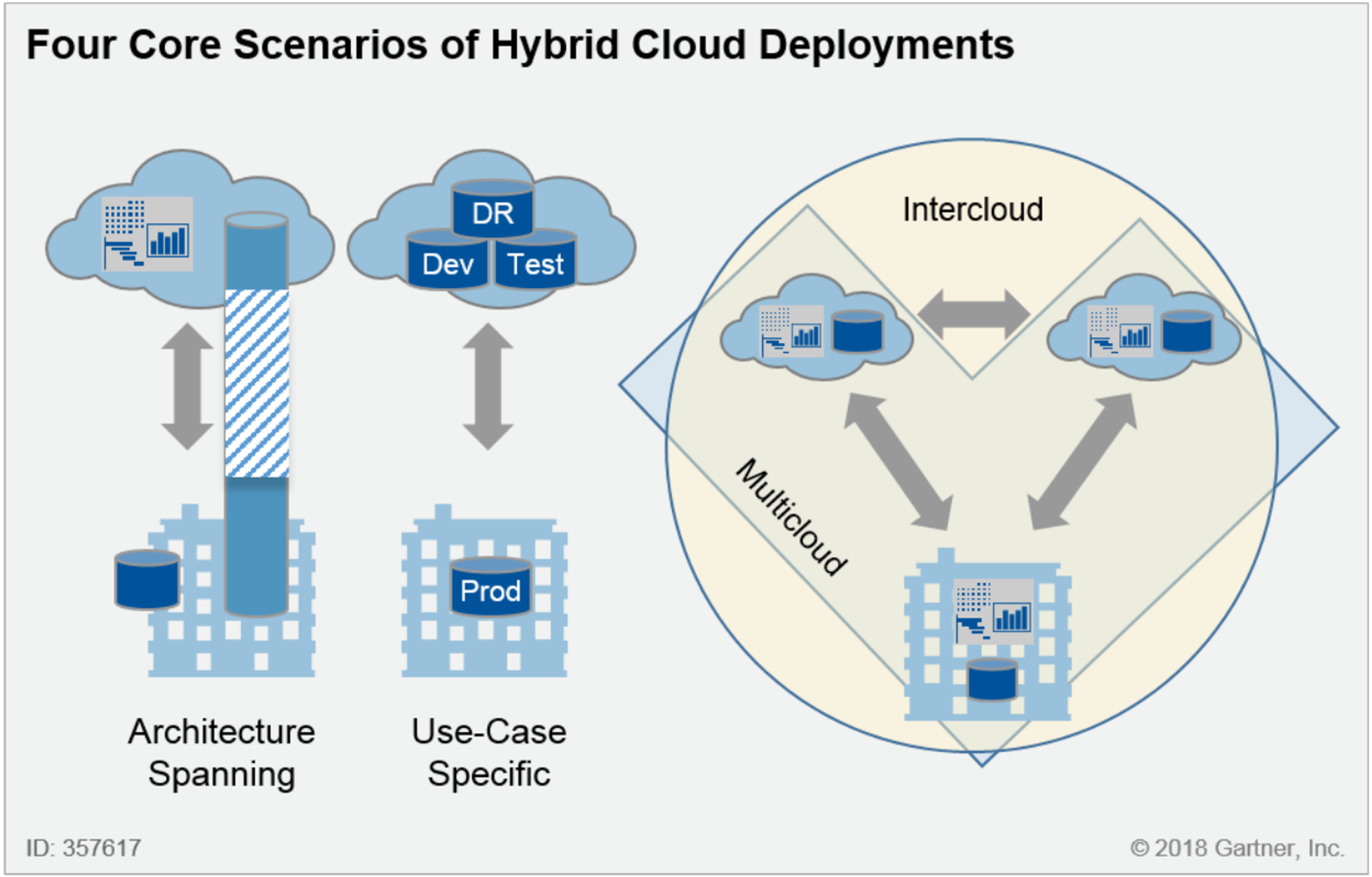
Architecture spanning
This strategy expands a business’s IT capacity by integrating with a cloud provider. It is useful in scenarios where additional resources are needed on demand or when data must be co-located for performance or compliance reasons. With this form of hybrid cloud, applications may run on infrastructure hosted by a cloud service provider while data remains within the company's self-hosted data centers.
Use-case-specific
This approach involves deploying versions of the same application in different locations based on the stage of development. For example, a company may use the cloud for development and testing because of its flexibility, while keeping production on specially provisioned in-house hardware. This setup works when the application does not rely on cloud-native services.
Multi-cloud
A multi-cloud approach involves running modern applications either entirely in the cloud or across both on-premises resources and multiple cloud providers. This model caters to a developer-first mindset, giving teams the freedom to choose the best technology for each task, whether it is offered by a cloud service provider or a custom, internal service.
Intercloud
Intercloud builds on the multi-data center, multi-residency design by enabling cross-cloud service provider traffic. This approach helps avoid vendor lock-in while taking advantage of best-of-breed services. For example, as Gartner notes, “Microsoft's Power BI might connect to a Salesforce database residing outside of the Azure cloud infrastructure.”
Each of the above types of hybrid cloud deployments come with their own considerations. Choosing the right approach for a given enterprise requires balancing service-level agreements (SLAs), cost, and technology offerings to align with enterprise needs.
Industry trends for hybrid cloud
Before diving into hybrid cloud trends, it is helpful to understand the broader cloud market. Gartner’s latest forecast projects worldwide end-user spending on public cloud services to grow 21.5% in 2025, with notable increases across service categories:
Worldwide Public Cloud Services End-User Spending Forecast, 2024-2025 (Billions of U.S. Dollars)
| Service | 2024 Spending | 2025 Spending | Growth |
|---|---|---|---|
| Infrastructure as a service (SaaS) | $169.9 | $211.9 | 24.8% |
| Platform as a service (PaaS) | $171.6 | $208.6 | 21.6% |
| Software as a service (SaaS) | $250.8 | $299.1 | 19.2% |
| Desktop as a Service (DaaS) | $3.5 | $3.8 | 11.1% |
| Total Market | $595.6 | $723.4 | 21.5% |
Source: Gartner (November 2024)
Public cloud spends for 2025
Cloud adoption remains strong, with enterprises making significant investments across multiple providers. AWS leads the market, with 49% of organizations running significant workloads on its platform, while Microsoft Azure follows closely at 45%:
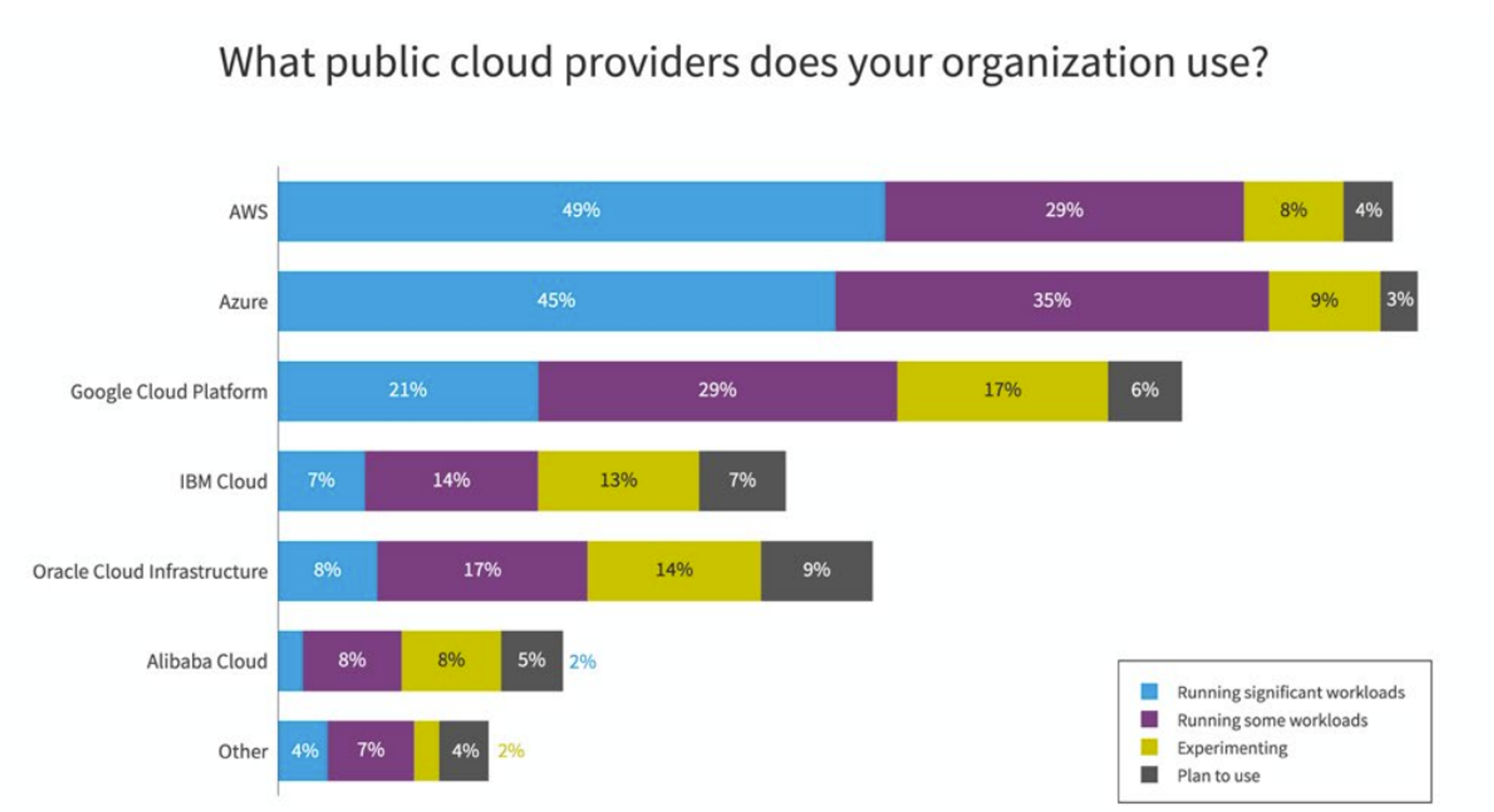
Source: Flexera State of the Cloud Report 2024
Enterprises are increasingly adopting multi-cloud strategies
Hybrid cloud adoption continues to rise, with 89% of enterprises citing a multi-cloud strategy and 73% of this subset citing hybrid cloud as a key component of their strategy:

Source: Flexera State of the Cloud Report 2024
Many industries rely on hybrid cloud models to balance security, compliance, and performance while leveraging the scalability of public cloud infrastructure. For example:
- Financial institutions store sensitive data on-premises for security and regulatory compliance, while using public cloud environments for real-time fraud detection and high-performance analytics.
- Healthcare organizations process patient data in the cloud while keeping sensitive records on-premises to meet HIPAA and other data protection regulations.
- Retailers and manufacturers use hybrid cloud solutions to optimize supply chain operations, ensuring high availability and disaster recovery readiness.
- Media and entertainment companies scale resources in the public cloud to handle traffic spikes while maintaining proprietary content on private infrastructure.
With global cloud spending projected to exceed $723 billion in 2025, enterprises will continue to invest in cloud solutions to optimize costs, enhance security, and maintain operational agility.
Read this whitepaper for more details
Hybrid cloud and DataStax Enterprise
DataStax Enterprise is the most powerful database designed for hybrid cloud. Whether public, private, or hybrid cloud, DataStax Enterprise easily spans across cloud regions and data centers with self-driving operational simplicity, allowing enterprises to easily deploy mission-critical applications across cloud environments without having to actually change anything about the applications.
A distributed cloud database enables you to leverage a hybrid, multi-cloud architecture to:
- Choose the services you want from each IaaS vendor with ease and ability
- Design your architecture with the cloud services you choose
- Geographically distribute data to meet governance and compliance requirements
- Implement services on your on-prem database and leverage resources from multiple clouds
- Seamlessly leverage tools offered by different IaaS vendors or move across vendors to scale for incredible data volumes, without downtime
- Protect apps and customer experience from service disruptions with the ability to replicate to on prem or across clouds, or evacuate regions due to outage concerns
Learn more about hybrid cloud
We have a variety of resources to help you continue learning about hybrid cloud deployments and distributed cloud databases:
Active everywhere, built for hybrid cloud
Relational database management systems (RDBMS) have served many enterprises for over 4 decades. Listen to our podcast episode on this subject to learn more.
Why your enterprise needs a cloud strategy
David Waugh, SVP of Market Development at DataStax talks about Hybrid-Cloud Strategy and uncovers the truth about hybrid-cloud deployments and hybrid databases — aren't they synonymous? Find out in this podcast!
The 4 superpowers of hybrid cloud databases
The market for cloud databases is on fire. According to a recent study, the global cloud database market hauled in $2.1 billion in 2015.
Hybrid cloud and e-commerce
Builders of ecommerce applications face unique challenges in today's hyper-connected, lightning-fast, zero-attention-span environment.
What is hybrid cloud? Is it just hype?
Get the full breakdown on the popular question that's on many enterprises' mind: What is Hybrid-Cloud?
The journey to hybrid cloud with DataStax Enterprise: 5 keys to success
Improving development agility, reducing time to market, avoiding cloud outages—there are many reasons to move to hybrid or multi-cloud.
FAQs
1. What is hybrid cloud, and how does it work?
Hybrid cloud refers to a computing environment that combines public cloud infrastructure with private clouds or on-premises data centers. This hybrid cloud approach allows businesses to leverage public cloud resources for scalability while maintaining sensitive data on-premises for security and compliance. Hybrid cloud solutions enable seamless integration between multiple environments, ensuring a unified platform for workloads.
2. What are the key benefits of hybrid cloud computing?
Hybrid cloud benefits include increased flexibility, cost efficiency, and improved disaster recovery capabilities. Businesses can use public cloud services for scalable compute and storage resources while keeping mission-critical applications in private cloud environments. Hybrid cloud infrastructure also supports business continuity by balancing workloads across multiple clouds and data centers.
3. How does hybrid cloud architecture differ from multi-cloud?
Hybrid cloud architecture integrates private and public clouds into a single, cohesive environment, allowing for data and workload portability between them. In contrast, a multi-cloud strategy involves using different cloud providers for separate workloads without direct integration. Hybrid cloud environments provide a more unified approach, ensuring better hybrid cloud management and interoperability between multiple environments.
4. What are the challenges of implementing a hybrid cloud model?
Hybrid cloud challenges include managing security across separate clouds, ensuring regulatory compliance, and integrating existing systems with new cloud infrastructure. Hybrid cloud management requires robust tools to monitor workloads, optimize storage resources, and maintain seamless communication between on-premises services and public cloud solutions.
How DataStax helps:
DataStax solutions—built on the open-source power of Apache Cassandra—are uniquely suited for hybrid cloud environments. With flexible deployment options, advanced security features, and native multi-cloud support, platforms like Astra DB make it easy to unify data and operations across on-premises and cloud infrastructure. Teams get the observability, scalability, and compliance readiness they need—without being locked into a single provider.
5. What are some real-world hybrid cloud examples?
Hybrid cloud platforms are widely used in industries that require both public and private cloud services. Common hybrid cloud examples include financial institutions storing sensitive data on-premises while leveraging public cloud environments for high-performance analytics, or healthcare organizations using hybrid solutions to ensure regulatory compliance while utilizing cloud computing for patient data processing.


